Introduction
Businesses are complex entities, often juggling multiple goals and tasks simultaneously. To streamline and optimize these intricate operations, organizations turn to Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN). BPMN provides a standardized visual representation of business processes, offering a common language that spans from business analysts to technical developers and business managers.
Understanding Business Processes and Goals
At the core of BPMN is the recognition that a business process is a series of coordinated activities aimed at achieving a specific business goal. This goal is the target that an organization aims to reach by executing the related business process efficiently.
In BPMN terminology, a Business Process Diagram (BPD) is used to define these processes. It is a network of graphical elements representing activities and the flow controls that dictate their order of execution.
The Purpose of BPMN
The primary objective of BPMN is to create a notation that is easily understandable by a diverse audience, ranging from business analysts to technical developers and business managers. It serves as a bridge between the conceptualization of a business process and its actual implementation.
BPMN achieves this through the development of a standardized Business Process Diagram (BPD) that incorporates graphical elements. These elements, categorized into Flow Objects, Connecting Objects, Swimlanes, and Artifacts, contribute to the creation of intuitive diagrams resembling familiar flowcharts.
Levels of BPMN Application
BPMN can be applied at three different levels:
- Descriptive Process Models: Suitable for high-level modeling, akin to traditional flowcharts.
- Analytic Process Models: Emphasizes the most commonly used concepts covered in BPMN training.
- Common Executable Process Models: Focuses on elements necessary for executable process models.
These levels cater to different stakeholders, ensuring that both the intricacies of implementation and the high-level overview are captured in the modeling process.
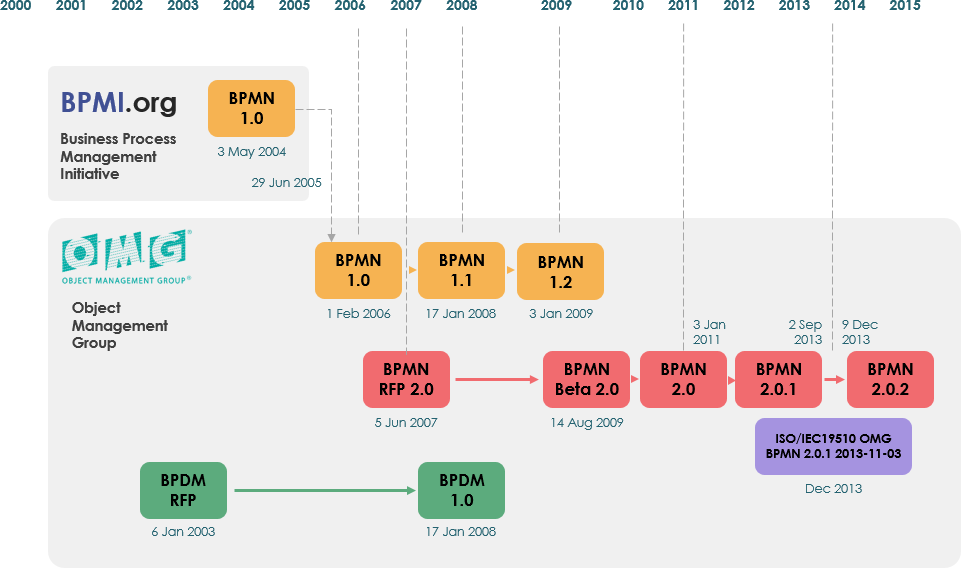
Evolution of BPMN
Originally developed by the Business Process Management Initiative (BPMI), BPMN has undergone significant evolution. The initial 1.0 specification was released in May 2004, with subsequent versions leading to the current standard—BPMN 2.0.2, published by ISO in December 2013.
Core Elements of BPMN
Flow Objects
BPDs consist of four basic categories of elements:
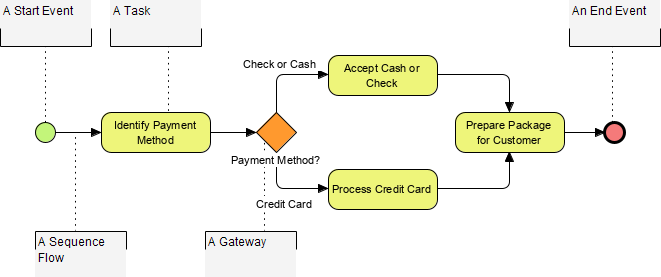
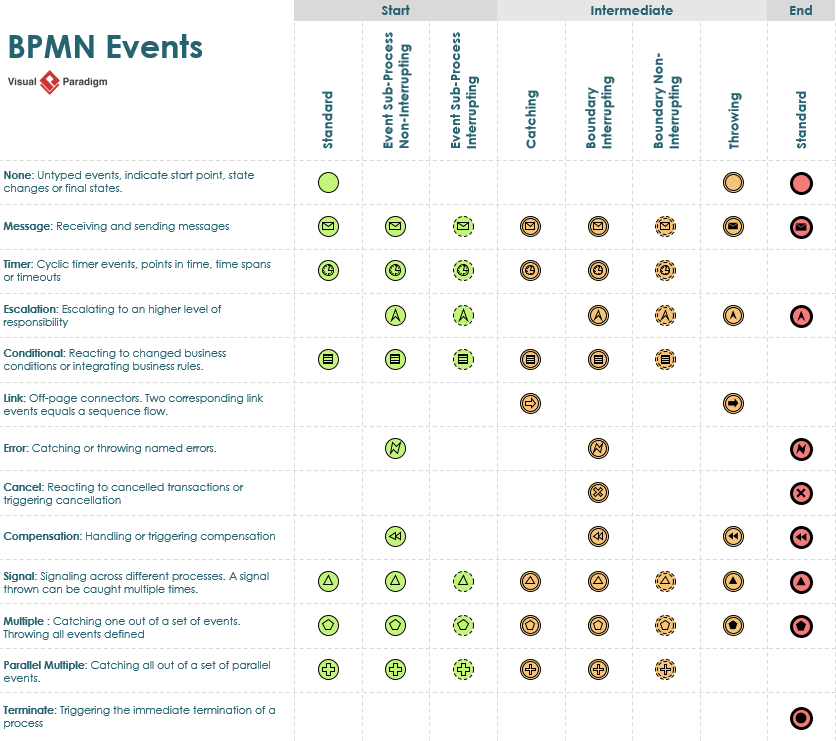
- Events: Represented by circles, events signify occurrences during a business process. They can be Start, Intermediate, or End events.
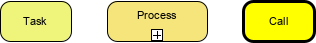
- Activities: Represented by rounded-corner rectangles, activities are generic terms for work performed by a company. They can be atomic (Task) or nonatomic (Sub-Process).
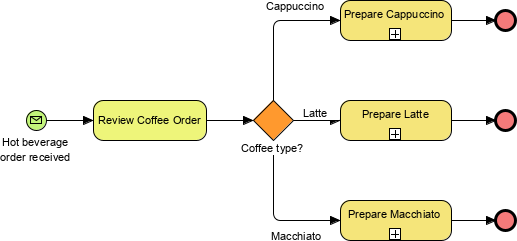
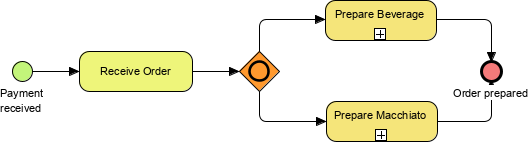
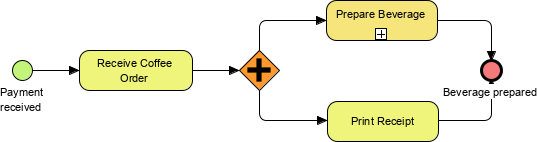
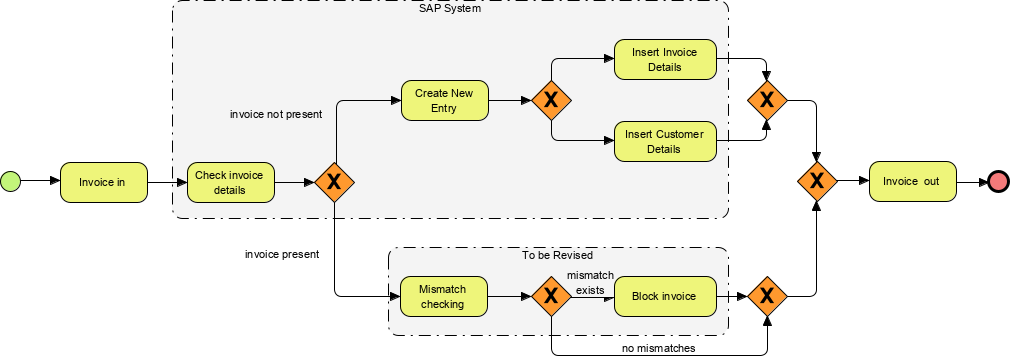
- Gateways: Represented by diamonds, gateways control the flow of Sequence Flow, determining decisions and paths forking, merging, or joining.
Exclusive Gateway Follow only one path
Inclusive Follow one or more paths
Parallel Follow all paths
Connecting Objects
Flow Object Summary
Events
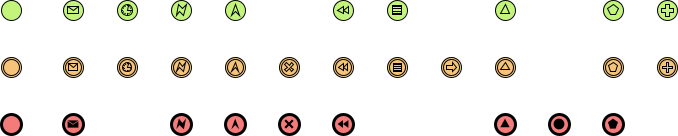
Activities
Gateways

BPMN Connecting Objects
The flow objects are connected together in a diagram to create the basic skeletal structure of a business process. There are three Connecting Objects that provide this function. These connectors are:
Connecting Objects establish the structure of a business process diagram:
- Sequence Flow: Solid lines with arrowheads represent the order of activities.
- Message Flow: Symbolizes information flow across organizational boundaries.
- Association: Annotations providing additional information relevant to the process.

Swimlanes
Swimlanes organize activities into visual categories:
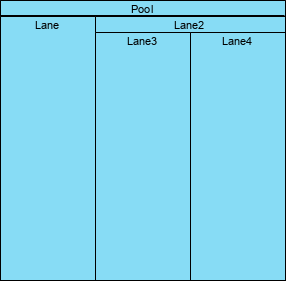
- Pool: Represents a participant in a process and acts as a graphical container for partitioning activities.
- Lane: A sub-partition within a Pool, used to organize and categorize activities.
Artifacts
Artifacts add flexibility and context to BPMN diagrams:
- Data Object: Shows how data is required or produced by activities.
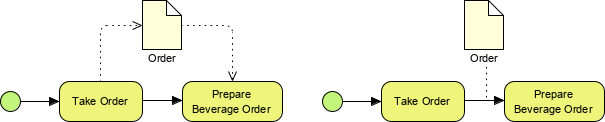
- Data Store: Represents where the process can read or write data persisting beyond its scope.
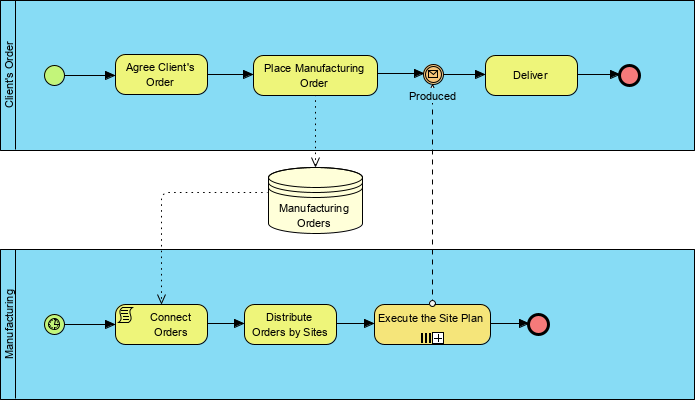
- Group: A visual grouping for documentation or analysis purposes.
- Annotation: Additional text information for the reader, explaining BPMN elements.
BPMN Notation: Simple or Complex?
BPMN allows for both simplicity and complexity within its notation. The notation’s flexibility enables modelers to convey intricate processes without sacrificing the clarity and familiarity of the basic diagrammatic language.
BPMN serves as a powerful tool for organizations to visualize, understand, and optimize their business processes. By providing a standardized and intuitive notation, BPMN facilitates effective communication across diverse stakeholders, ultimately contributing to the successful execution of business goals.
An Ideal BPMN Tool: Why Visual Paradigm
Visual Paradigm stands out as an ideal BPMN tool for several reasons, making it a top choice for organizations seeking efficient and comprehensive business process modeling solutions.
- Intuitive Interface: Visual Paradigm offers an intuitive and user-friendly interface, ensuring that both business analysts and technical developers can easily navigate and use the tool. This accessibility contributes to a seamless collaborative environment where stakeholders can actively participate in the modeling process.
- Comprehensive BPMN Support: Visual Paradigm provides extensive support for BPMN, covering all the essential elements of the notation. This includes Flow Objects, Connecting Objects, Swimlanes, and Artifacts, allowing users to create detailed and accurate Business Process Diagrams (BPDs).
- Flexibility for Various Levels of Abstraction: The tool supports different levels of abstraction, making it suitable for high-level overviews as well as detailed, executable process models. This flexibility ensures that organizations can use Visual Paradigm across various stages of the business process lifecycle.
- Collaboration Features: Collaboration is crucial in the business modeling process. Visual Paradigm offers collaborative features, allowing multiple users to work on the same project simultaneously. Real-time collaboration enhances communication among team members, leading to more efficient and accurate business process modeling.
- Integration Capabilities: Visual Paradigm integrates seamlessly with other development tools and platforms, providing a holistic approach to business process management. This integration capability ensures that BPMN models can be seamlessly incorporated into broader development and management workflows.
- Rich Documentation and Reporting: Visual Paradigm enables users to generate rich documentation and reports from BPMN models. This feature is essential for communication with stakeholders, project documentation, and compliance purposes.
- Continuous Updates and Support: Visual Paradigm is known for its commitment to continuous improvement. Regular updates and responsive customer support ensure that users have access to the latest features and assistance when needed.
- Training and Resources: Visual Paradigm offers training resources, tutorials, and documentation, supporting users in mastering BPMN modeling techniques. This commitment to user education enhances the overall user experience and proficiency with the tool.
- Scalability: Whether for small teams or large enterprises, Visual Paradigm scales effectively to meet the needs of different organizations. This scalability ensures that the tool remains a viable solution as businesses grow and evolve.
Visual Paradigm is an ideal BPMN tool due to its intuitive interface, comprehensive BPMN support, flexibility, collaboration features, integration capabilities, rich documentation, continuous updates, and scalability. These features collectively make Visual Paradigm a powerful and reliable choice for organizations seeking to streamline their business process modeling efforts.